On March 13th 2013 Google announced that they were shutting down Google Reader from July 1st. As a big RSS user I started looking around for an alternative a few days later and settled on using the web-based Newsblur. Now I’ve been using it for close to a month I thought I’d give a quick review.
How and Why RSS?
Before I do the actual review I thought I’d give a quick overview of Why I use a RSS reader. I think Marco Arment put it well when he wrote:
RSS is best for following a large number of infrequently updated sites: sites that you’d never remember to check every day because they only post occasionally, and that your social-network friends won’t reliably find or link to.
Which is very much the case with me. I read relatively obscure but interesting blogs that are not massively retweeted or linked to. I read enough of them that it isn’t practical to visit them every day to check for updates (which may only happen every few weeks) and I follow enough people on twitter (145) that I will sometimes skip a few hundred tweets that happened overnight so I could miss a tweet announcing a blog post (assuming I want to follow that persons tweets).
A specific use case I saw is for web comics. Instead of me checked the half-dozen web-comics I follow every day for a new stripe they all appear automatically in my reader.
Getting Started with Newsblur
To switch from Google reader to Newsblur was fairly simple. From Google reader I went to “settings” and then “Import/Export” and exported my information via Google “takeout”. Google then gave my a zip file which contained a subscriptions.xml file and some .json files.
I then setup a Newsblur account. Currently Newsblur offers free accounts and paid accounts. Free accounts are limited to just 64 feeds being active and update less often. Paid accounts cost $US 24/year and have unlimited sites, more updates and some sharing options. Once you create your account you can import you subscriptions.xml (call and OPML file) and you will see you previous subscriptions. After a couple of days using it I signed up to a one year subscription.
If you don’t have an old RSS reader you can just grab RSS feeds from sites you read. Look our for the RSS symbol or use your browser to find the RSS URL of the sites you want to follow.
Newsblur’s Interface
I found Newsblur’s interface to a little clunky but usable.
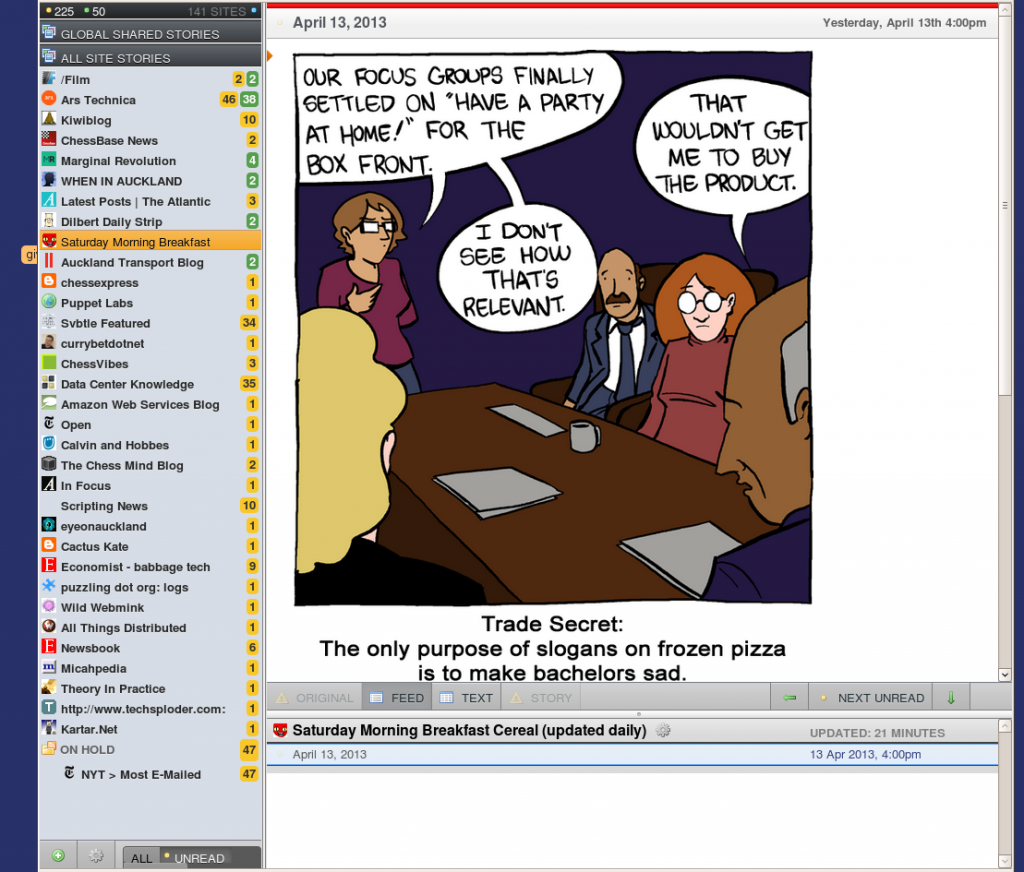
The left hand sidebar has my various feeds (the number is how many unread articles are in each) . The main pane on the right has the article I’m reading and the bottom right pane has the list of articles in my current feed (just the one I am reading in this case). The go to feeds you click on the name of the feed on the left and it loads in the right-hand panes.
The interface above shows i follow 141 sites and I have 225 unread articles. The “Ars technica” site (2nd from the top) is an example of a site I’ve used the built-in filtering function with. There are 37 articles I’ve filtered to “good”, 46 filtered to neutral and another 77 completely hidden ones I’ve filtered out. The filtering is fairly simple and works on keywords, authors or titles of articles. Sites which have good tagging are easiest to filter while those that don’t (eg slate.com) are a lot harder. This is a feature that Google reader never implemented and is very useful for readers sites where their are whole groups of posts you want to exclude (eg gaming articles on Ars Technica).
One of the bugs with the interface is that their are a lot of different option menus ( the “cog” at the bottom left, the “cog” in the feed pane next to the feed’s name, right clicking on a feed name) which are a bit confusing. There is even a dev.newsblur.com which has a preview of the upcoming interface . At least once I’ve switched the the “dev” site to fix a setting I couldn’t change in production.
Overall Impression
I’m fairly happy with Newsblur as a replacement for Google reader.
- Immediately after Reader announced their shutdown the site was overwhelmed with new customers but over the lat month they have expanded capacity and are now pretty stable and fast
- The site owner (1 person does everything) is fairly responsive to bug reports and help requests
- The interface is improving and being worked on
- The company appears to have a sustainable business model
- There are a good set of short-key keys to speed up reading.
- The filtering is very useful.
A few rough areas
- The interface is still a bit of a mess and has some bugs, hopefully the new release will improve
- I’ve found a few feeds are completely broken on Newsblur (eg James Hamilton’s Perspectives) but seem to work okay when I test them directly. Unfortunately Newsblur probably doesn’t have the manpower to fix these one by one.
- If you are a big using of the sharing and highlighting functions of Google Reader then Newsblur’s equivalent may be short of what you need. I don’t use these however.
- There is no “sort by magic” function that Google Reader had, but this filtering is a good replacement in most cases.
But I think the site is more than usable and getting better and I definitely recommend it to others.

